Sales
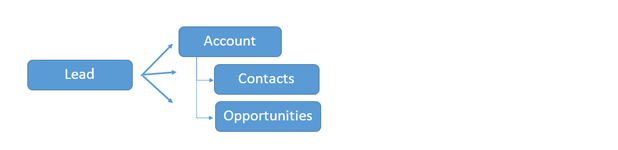
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is designed to support the sales process from acquiring a new lead through the close of a sale. CRM has a place to store the contact information for new leads, a place to track the follow-up communications (such as Phone Calls, Emails, and Appointments), and the ability to qualify a Lead into an Account, Contact, and Opportunity.
CRM keeps Leads in a separate area (essentially quarantined) in order to ensure your main database of Accounts and Contacts does not get cluttered with people your organization doesn’t know.
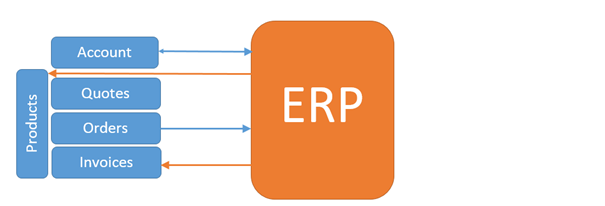
As part of the Opportunity, you may create a Quote in CRM and convert that to an Order and an invoice. CRM’s Product Catalog provides the basis for this process. Organizations using this functionality often have an integration with their financial software or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. In this way the product catalog and pricing has a single source, is kept up-to-date, and the complexities of ordering and invoicing are handled appropriately.
Below represents a typical integration between CRM and ERP.
The end of a typical sales process is the close of the Opportunity as Won or lost. If the opportunity is Won, the Relationship Type on the Account is often changed from Prospect to Customer.
Configuring Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales Process
Every organization that implements CRM for sales must spend a little time analyzing their unique processes and configuring CRM to reflect that. This might mean just changing a few fields or it might mean significantly modifying the forms and view, deciding to add new record types, and/or deciding to disable unused features.
For example, out-of-the-box CRM most closely supports a Business-to-Business (B2B) sales process with a longer sales cycle. If that describes your organization, you will have an easier time using CRM out-of-the-box with only minor business process analysis and configuration.
Other organizations that might be Business-to-Consumer (B2C) or have a shorter sales cycle should analyze their process and consider what customization may be needed. Therefore, each organization must carefully evaluate their own sales process to determine how much CRM can be used out-of the-box.
Understanding Leads
A lead represents any person or organization that a company might have the potential to do business with. Microsoft Dynamics 365 is used to store data about that lead. In fact, creating a Lead record of information about a new lead is often the first step users take in the sales process. For instance, if your company receives an inquiry on your website contact form about your product offerings, you would use a Dynamics 365 lead record to collect and store information about that person or business.
TIP! Not every organization will use leads. For help on determining whether your organization should use leads, refer to the section on Should You Use Leads?
Elements of a Lead
The lead record contains basic data such as the organization name, contact information, or how a lead was generated (often called the Lead Source). Organizations often customize the lead record to collect data relevant to their sales process.
Working with Leads in Dynamics CRM
Creating Leads
1. In your Lead View, click New. This will bring up a new Lead record where you can enter data manually.
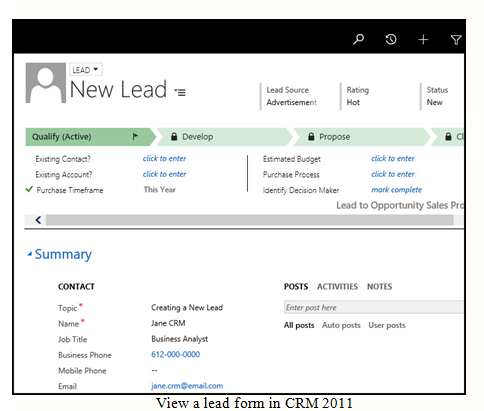
2. Fill out required data such as Topic and Name, as well as any additional data you may have. Contact information is particularly important for following up and qualifying leads.
Tip! Sometimes leads are entered into Dynamics CRM by more than one user, creating duplicate records. Learn more about duplicate detection and removing duplicate records from the system.
Assigning Leads
You can assign leads a couple of ways. One would be to auto-assign leads from workflows. But you can also assign individual leads manually.
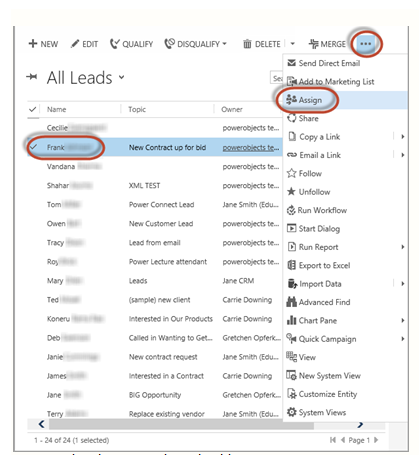
To assign a lead or several leads to an individual, open your Lead View and select the leads you want to assign. Select the Ellipses in the command bar and click the Assign button in the drop down.
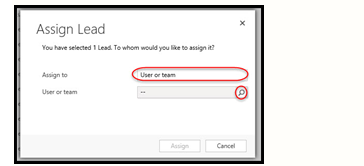
This will open a dialog box. The Assign to field will default to the Me option, but clicking on that field will change it to the User or Team option, and you can use the look-up to search for any user or team you wish to assign it to.
Adding Activities to Leads
To add an activity to a lead, open a Lead record, navigate to Activities and choose which Activity you would like to add for that lead. Common activities are Tasks, Phone Calls, E-mails, Appointments, and Booking Alert.
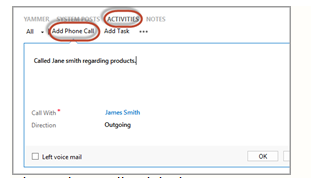
Qualifying Leads in Dynamics CRM
When you Qualify a lead, you determine whether or not that lead is a good candidate for doing business with. At that point, the lead will be converted into a Contact, Account, or Opportunityor a combination of these three record types. If you determine that they are not good candidates for any of these actions, you will Disqualify the lead, which means that they are not currently a good candidate to do business with.
To qualify a lead: 1. In your Lead view, open the Lead record and you can either Qualify or Disqualify the lead in the command
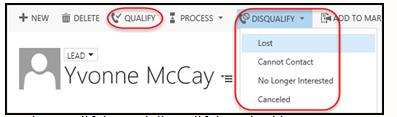
2. If you qualify the record, you convert the lead into either an Account, Contact, or Opportunity record, or a combination of those record types.
- If you Qualify a record, the original lead record is deactivated.
- If you Disqualify a record, you’ll have the option of entering a reason why it is disqualified – Lost, Cannot Contact, No Longer Interested, or Canceled. Then the lead record will be deactivated and you will not find it in your list of active leads.
Tip! Every organization will have its own criteria for determining whether or not a lead is qualified. It is important to have all Dynamics 365 users be consistent with the criteria
Working with Opportunities
- Creating new Opportunities
- Working with the Process-Based Form
- Automating and Analyzing the Sales Process
- Closing Opportunities
Creating New Opportunities
A. From the command bar in the Opportunities section
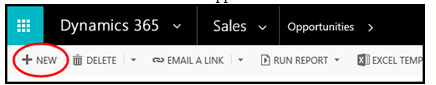
View creating a new opportunity in CRM 2011
B. Converting a tracked email from Outlook
1. In email, click on Track in the ribbon. Doing this will activate the Convert To button.
2. Click on Convert To > Opportunity
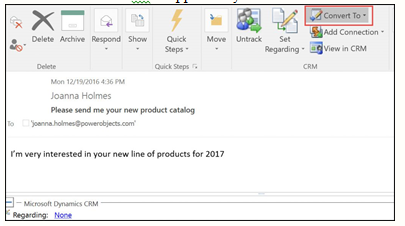
3. Click on the customer look up and select the appropriate customer.
4. Complete filling out the opportunity as usual.C. Converting a CRM activity
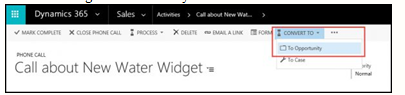
D. Qualifying a Lead

E. Converting campaign responses
1. In the top navigation of a campaign response record, click the Convert Campaign Response button. A new window will open.
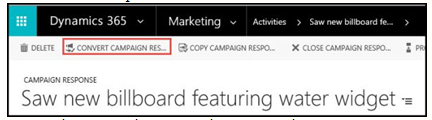
2. Select the “Create a quote, order, or opportunity for an account or contact” radio button.
3. Look up the account, select the opportunity option, and set a currency.
4. Click Ok.
Creating opportunities with user-provided revenue:
- Navigate to the Opportunities view.
- Click on New in the command bar.
- Topic: Enter a short description.
- Potential Customer: You choose a contact or an account. If you do B2B, your potential customer will be an account. If you do B2C, it will be a contact.
- Revenue: Under the Product Line Items section of the form, choosing User Provided will allow you to manually enter Estimated Revenue. Choosing System Calculated requires the use of the product catalog.
- Estimated Revenue: This field feeds the sales pipeline. Once an opportunity is won or lost, users can enter Actual Revenue.
- Owner: This defaults to the user creating the opportunity. Typically the owner is the sales person who is responsible for closing the sales
Working with the Process-Based Form
The release for CRM 2011 introduced a new user interface with process-based forms for accounts, contacts, leads opportunities and cases and is also known as a Business Process Flow. In Dynamics 365, there are several pre-configured business process flows which you can use as they are, or edit them to suit your unique business needs. You can even have multiple processes and switch between them if you have business scenarios that call for a different process to be followed by simply clicking the Process button on the command bar.
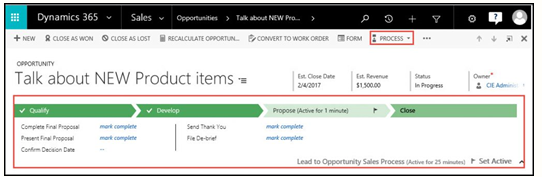
With business process flows organizations can guide sales users through a process and stages. The Lead and Opportunity have been combined onto one form and one process. The first stage is when the record is the lead and you can convert the lead to an opportunity by proceeding to the next stage.
Note: when you qualified a lead in a previous versions a window would pop open allowing you to select whether to create an opportunity, account and/or contact. This window no longer exists.
As you move to the next sales stage the fields that are right below the stages change. These can be customized. Notice that the fields change when you move the opportunity from the Develop to Propose stage. You can tell which stage the opportunity is currently at by the flag icon on the active stage.Develop Stage

Customize the Process Form:
- Open the entity form that you want to customize.
- Select Process on the command bar. Choose Edit Process.
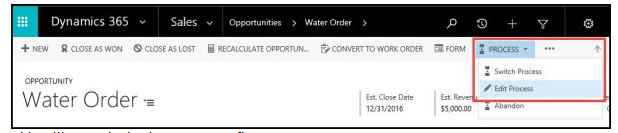
This will open the business process flow.
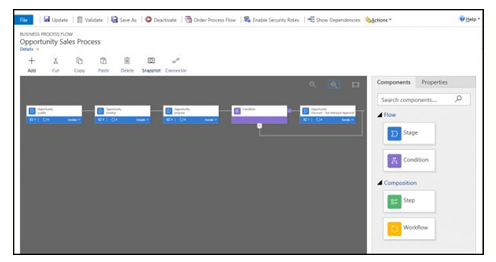
- From here you can drag components at right to modify the process, add steps to existing stages, insert conditions, and add workflows to either specific stages of the process, or set them as a Global Workflow item if you want to trigger a workflow based on the start of a process, or completion of a process. It’s important to note the workflow component must be based on the same primary entity as the process.
- You can also enable security roles for specific processes. For example, maybe your service reps can read the Opportunity process but can’t make any changes.
- Once you’ve completed your edits, click Update, and your new edits to the existing process will be available.
To create a brand new process navigate to Settings > Processes and click the New button in the command bar. This will open the Create Process dialog box. Give the new process a name, set the Category to Business Process Flow, and in the Entity list select the entity you are creating the process for.
Automating and Analyzing Sales Processes
Many organizations use workflow to help automate their sales process. If used correctly, automation offers the following benefits:
- Reduce data entry for sales team
- Ensure sales team follows consistent sales processes and protocol
- Alerts
- Inform management of important opportunities
- Procurement of possible inventory strain
- Sales Executive of nearing estimated close date
- Escalation based on neglected opportunities
- Activity Creation
- Activities based on stage or other parameters (Estimated Revenue)
- Activity completion advances sales stages
- Update customer records based on Opportunity
Analyzing the Sales Process
Dynamics 365 offers a number of ways for sales teams to analyze their sales data. With the exception of Custom Reports created in SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS), power users can build the rest once they have insight into their data and how to accomplish this in Dynamics 365.
Options for analyzing data:
- Charts
- Dashboards
- Views
- Goals
- Excel
- Report Wizard reports
- Out of box reports
- Custom reports (SSRS)
Company leadership can use reports and dashboards to gain oversight into:
- When revenue will hit
- What opportunities have been neglected
- What industries/verticals have potential
- How individual sales executives are doing
- When they need to ramp up staffing
- How close you are to organizational goals
Closing Opportunities
Effective management of opportunities requires users close opportunities upon win or loss. When an opportunity is won or lost users are prompted to enter Actual Revenue and Actual Close Date. The competitor who won the opportunity can be entered when an opportunity is lost. Once it is won or lost it is marked as complete and cannot be modified. However, opportunities can be reopened if necessary. The Actual Revenue is reflected in many reports and charts throughout Dynamics 365.
Closing an Opportunity can be done from the Opportunity view or from within the Opportunity record.
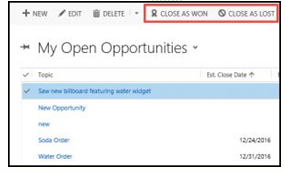
From the Opportunity view:
- Select the Opportunity in the view
- Click on Close as Won or Close as Lost in the command bar.
From within the Opportunity record:
- Open the Opportunity record
- Click on Close as Won or Close as Lost in the command bar. This generates the Close Opportunity dialog where users enter the Actual Close Date (this defaults to the current date), Actual Revenue (this defaults to the Estimated Revenue for won opportunities and as zero for lost opportunities), and Competitor (this is only for lost opportunities and indicates who won it)
- Click OK